What is a Cell?
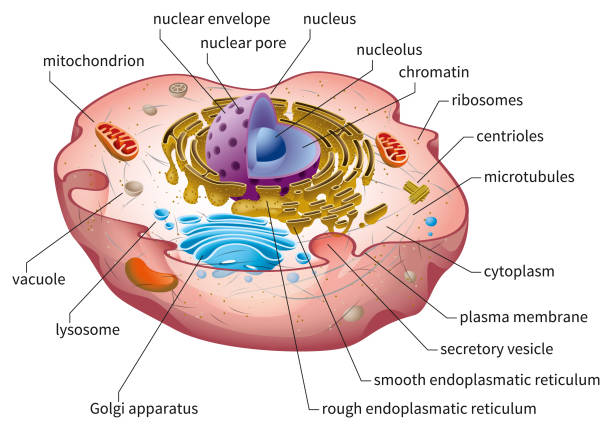
A cell is the smallest unit of life and is responsible for carrying out all the metabolic tasks in a living organism. Cells are made up of molecules that interact with each other and with their environment to create the structure and function of the cell. In this article, we will explore what cells are, how they work, and some of the ways they can be used in research and medicine.
What is a Cell?
A cell is the smallest unit of life in an organism and contains the genetic information that allows an organism to grow, function and reproduce. Cells are made up of a nucleus and a number of organelles, including the mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum.
A cell is the smallest unit of life and is what makes up all living things. Cells are small because they have no organs or other body parts. Cells come in many shapes and sizes, but all cells have the same basic structure. Cells are made of protein and DNA. Proteins are made of amino acids and DNA is made of RNA and proteins.
Cells use energy to do things like grow, work, and reproduce. Cells get their energy from food or light. Cells use oxygen to make energy and to create waste products. Cells also need water to stay alive.
Cells are important because they can divide many times to create new cells. This is how we grow and change as people.
You may also like;
- Best Podcast For College Students | Top 5
- Learning App For Kids in 2022 | The Best 5
- How to contribute to your community
- How to use keyword research for SEO
- Was Michelangelo Gay?
Frequently Asked Questions about What is a Cell
How do Cells Reproduce?
The process of reproduction in cells is quite complicated, but it all starts with the division of the cell. The cell wall is broken down and the cell divides into two. Then each daughter cell takes on the same characteristics as the parent cell.
How do Cells Communicate with Each Other?
Signaling pathways play a crucial role in how cells coordinate their activities and communicate with each other. Signaling pathways can be divided into three types: secreted, membrane-associated, and cytoplasmic. Signaling pathways that are secreted from cells can travel outside the cell and interact with other cells or extracellular matrix proteins.
Membrane-associated signaling pathways take place within the cell membrane and can be activated by different stimuli such as ATP, a molecule that is generated during energy metabolism. Cytoplasmic signaling pathways are activated within the cell cytoplasm and often involve the activation of transcription factors.
Why is it called a Cell?
Cell (plural: Cells) is traditionally a biological unit of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. It is the smallest unit of life, consisting of one or more cells. The name derives from the Latin word for “little room”, in analogy with the larger units of animal and plant life.
What is cell and its types?
There are two types of cell:
- Eukaryotic: which has a nucleus,
- Prokaryotic cells, which do not have a nucleus, but a nucleoid region is still present.
Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms, while eukaryotes may be either single-celled or multicellular.
Conclusion
A cell is the basic building block of life. Cells are able to reproduce, secrete chemicals, and participate in metabolism. There are more than 100 different types of cells in the human body.
For more general updates, follow dailygam.com
Last Updated 3 years by